27 Mar 2025
BlogOverview
This article delves into the seven principles of sustainable construction, highlighting their crucial role in tackling environmental challenges and enhancing societal benefits. These principles are not merely guidelines; they are fundamental for achieving sustainability within the building sector. By promoting resource efficiency, energy conservation, and the use of eco-friendly materials, they play a pivotal role in climate change mitigation and improving the quality of life.
Why are these principles essential? They address the pressing need for sustainable practices in construction, ensuring that we meet the demands of today without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. Each principle contributes uniquely to a holistic approach to sustainability, fostering a built environment that is both resilient and responsive to the challenges we face.
In conclusion, understanding and implementing these seven principles is imperative for anyone involved in the construction industry. By embracing these practices, we can significantly impact our environment and society, leading to a more sustainable future. It is time to act, let us commit to these principles and drive the change necessary for a better tomorrow.
Introduction
As the world confronts urgent environmental challenges, the construction industry finds itself at a crucial crossroads. Sustainable construction stands out as a beacon of hope, presenting innovative strategies that not only reduce ecological footprints but also promote societal well-being. The escalating demand for eco-friendly building practices underscores the growing importance of sustainable construction.
By leveraging renewable materials, adopting energy-efficient designs, and applying waste reduction techniques, the industry is equipped to tackle pressing issues like climate change and resource depletion.
As we explore the fundamental principles and practices of sustainable construction, it becomes clear that the path forward is not merely a necessity; it is an opportunity to cultivate a resilient and environmentally responsible built environment for future generations.
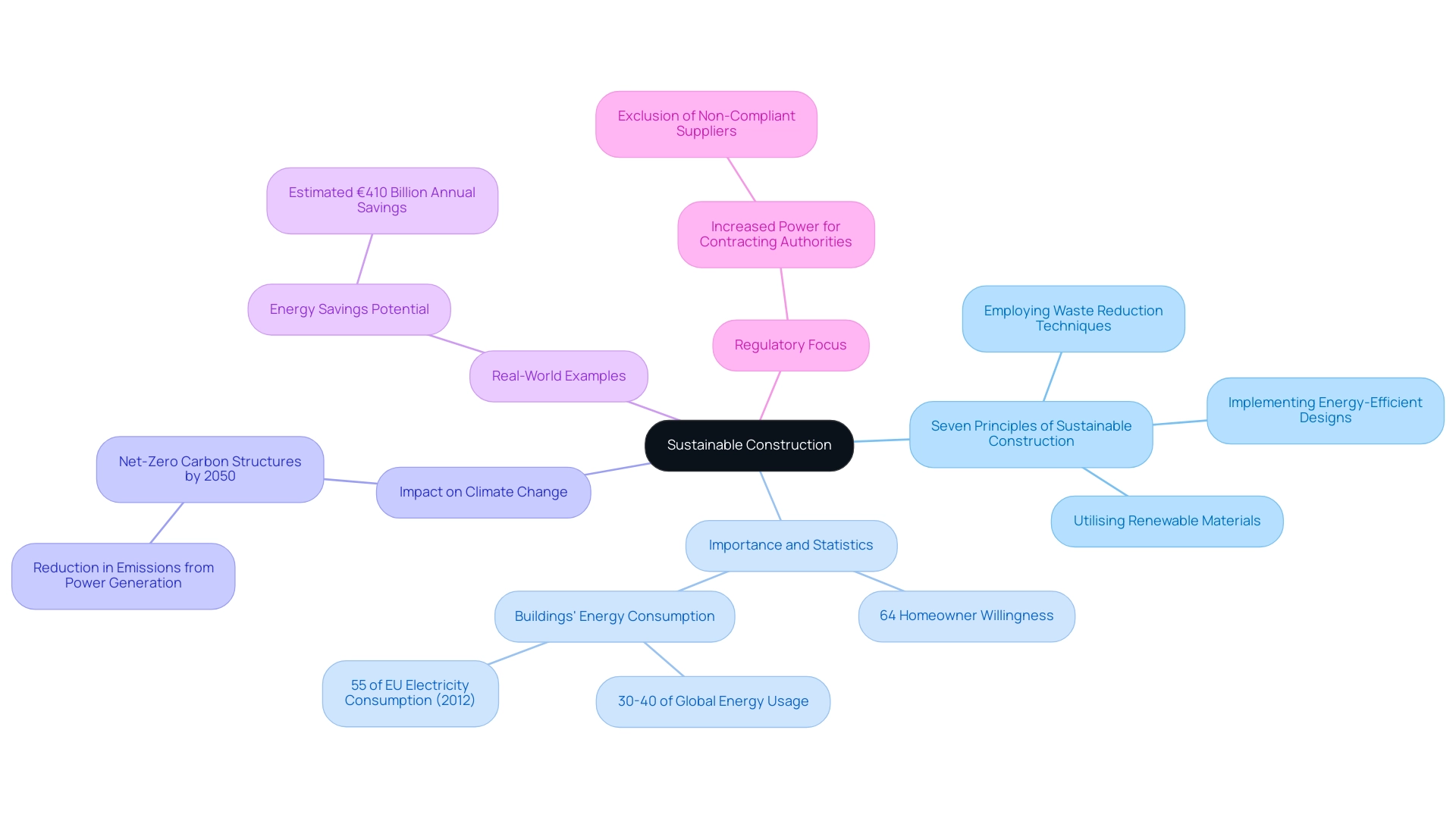
Understanding Sustainable Construction: Definition and Importance
Sustainable development is defined as the method of designing, erecting, and operating structures, which mitigate adverse environmental effects while enhancing societal benefits. This holistic approach incorporates a variety of strategies that reflect these principles, such as utilising renewable materials, implementing energy-efficient designs, and employing waste reduction techniques. The importance of sustainable building, as underscored by these principles, lies in its ability to address pressing global challenges, including climate change, resource depletion, and rapid urban development.
In 2025, adherence to the seven principles of sustainable construction is more crucial than ever. Recent statistics reveal that 64% of homeowners are willing to pay a premium for residences in green communities, highlighting a growing demand for environmentally responsible construction practices. Furthermore, the infrastructure industry accounts for a significant share of global energy usage, with structures representing 30-40% of overall energy consumption worldwide.
In the European Union alone, buildings accounted for 55% of electricity usage as of 2022, emphasising an urgent need for eco-friendly solutions. The United Nations has indicated that achieving net-zero carbon structures by 2050 necessitates a substantial reduction in emissions from power generation.
Real-world examples illustrate the effectiveness of the seven principles of sustainable construction in minimising environmental impact. For instance, the integration of cutting-edge technologies in design and assembly can lead to significant energy savings, with estimates suggesting possible reductions of €410 billion annually in global energy expenditures. This not only aids in lowering emissions but also enhances the overall efficiency of buildings.
Edmond Shipway plays a pivotal role in this arena by providing comprehensive project management and cost advisory services that prioritise sustainability. By embedding eco-friendly practices into their project management strategy, Edmond Shipway ensures that building initiatives not only adhere to the seven principles of sustainable construction but also yield environmental benefits.
The impact of these principles on climate change and resource depletion is profound. By prioritising the seven principles of sustainable construction, the building sector can significantly contribute to the goal of achieving net-zero carbon structures by 2050, which requires a substantial reduction in emissions from energy production. Additionally, recent developments indicate that contracting authorities will gain increased power to exclude suppliers who fail to meet required standards and legal obligations, including those related to health, safety, and sustainability.
This regulatory focus underscores the importance of embracing the seven principles of sustainable construction in the building sector.
In conclusion, the significance of these principles in 2025 is unmistakable. They are essential for tackling climate change, conserving resources, and enhancing the quality of life for both current and future generations. As Edmond Shipway focuses on delivering high-quality services and fostering strong client relationships, their commitment to eco-friendly practices will be crucial in shaping a resilient and environmentally responsible built environment.
Key Elements of Sustainable Construction Practices
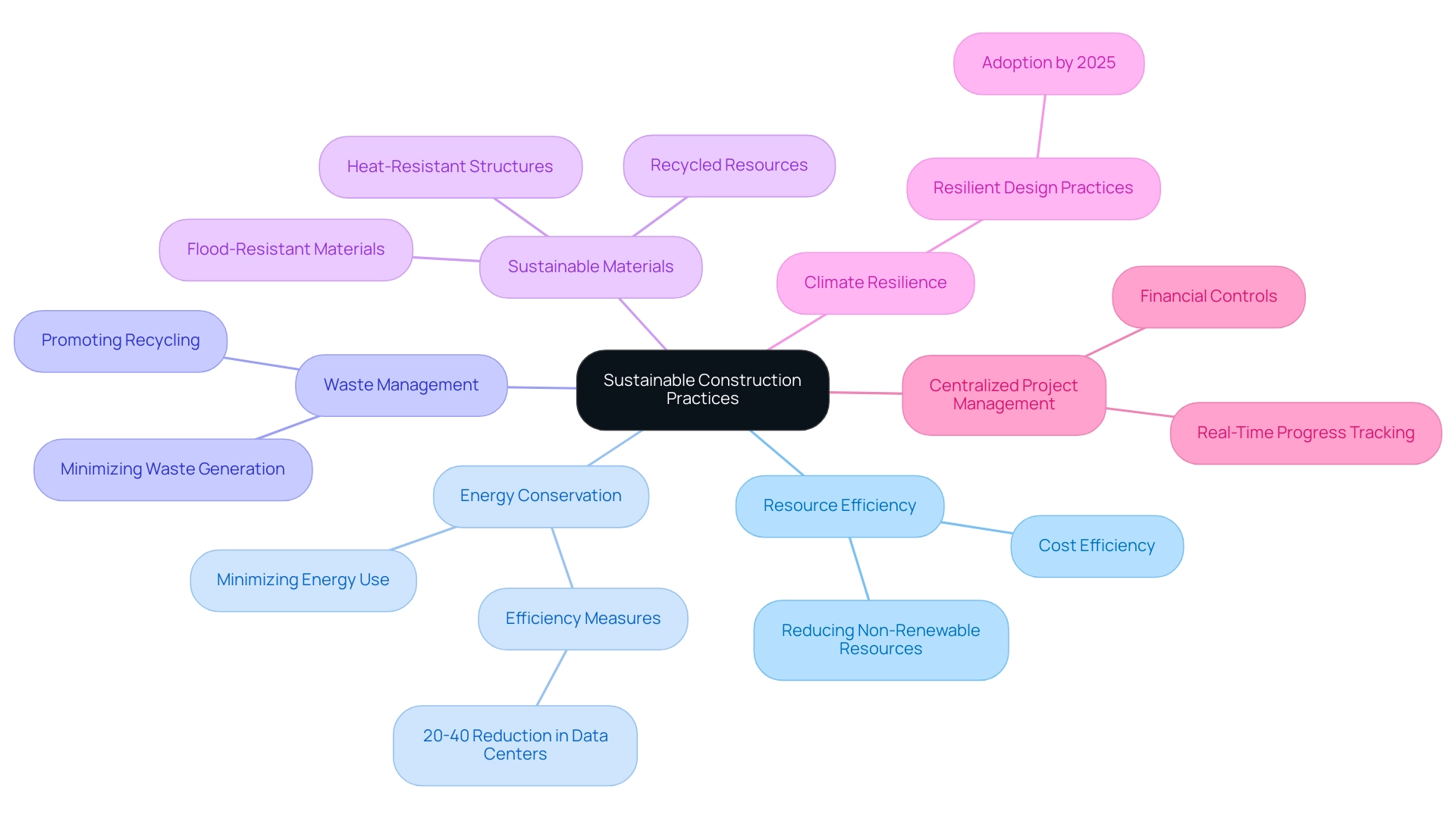
Key elements of sustainable building practices encompass resource efficiency, energy conservation, waste management, and the use of sustainable materials. As the building sector faces pressures to adapt to shifting market dynamics and environmental challenges, resource efficiency has become increasingly critical, focusing on reducing reliance on non-renewable resources.
Energy conservation, aimed at minimising energy use throughout a building’s lifecycle, is projected to gain traction in 2025 as firms implement innovative strategies aligned with sustainability goals. Research from the Sustainable Cities and Society (SCS) indicates that data centres can achieve a 20-40% reduction in energy consumption through efficiency measures, highlighting substantial potential for energy savings across various sectors.
Effective waste management strategies are essential for minimising waste generation and promoting recycling, thus contributing to a circular economy within the building industry. The selection of sustainable materials, including recycled or rapidly renewable resources, plays a critical role in mitigating the environmental impact of construction projects. For instance, the incorporation of flood-resistant materials and structures designed to withstand extreme heat is becoming standard practice as climate resilience takes precedence in building design.
The case study titled ‘Building for Climate Resilience’ illustrates that by 2025, these resilient design methods are expected to be widely adopted, particularly in areas vulnerable to extreme weather events.
Centralised oversight in project management provides a single source of truth for stakeholders, enhancing real-time progress tracking and financial controls, which are essential for sustainable building methods. Together, these components create a comprehensive approach to sustainability in the built environment, ensuring that building practices not only meet current needs but also safeguard future generations. The importance of resource efficiency and energy conservation cannot be overstated, as they are vital to achieving long-term sustainability objectives and enhancing overall project performance.
The 7 Core Principles of Sustainable Construction
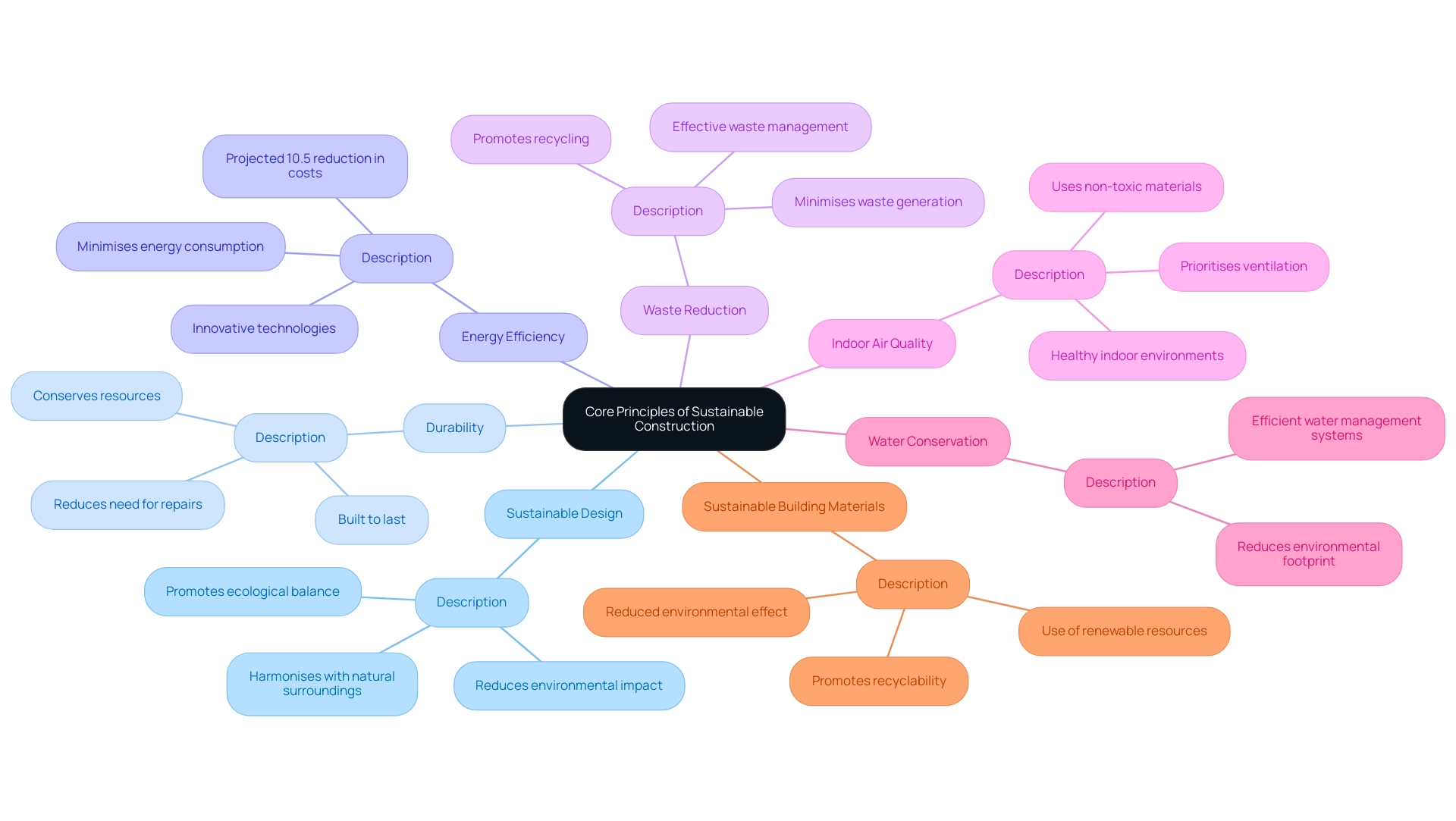
The seven principles of sustainable construction are essential for fostering environmentally responsible practices. They include:
- Sustainable Design: This principle emphasises the creation of structures that harmonise with their natural surroundings, promoting ecological balance and reducing environmental impact.
- Durability: Ensuring that structures are built to last is crucial. Durable structures not only withstand the test of time but also reduce the need for frequent repairs and replacements, ultimately conserving resources.
- Energy Efficiency: Minimising energy consumption is a key focus, achieved through innovative technologies and design strategies. In 2025, advancements in energy-efficient building design are projected to significantly lower operational costs, with studies indicating potential reductions of up to 10.5% in the first year alone. This aligns with the growing recognition that eco-friendly building practices can lead to substantial financial benefits.
- Waste Reduction: Implementing effective waste management strategies during building is vital. This principle encourages the minimisation of waste generation, promoting recycling and the use of eco-friendly materials.
- Indoor Air Quality: Creating healthy indoor environments is paramount for occupant well-being. Sustainable construction practices prioritise ventilation and the use of non-toxic materials to enhance air quality.
- Water Conservation: Efficient water management systems are integral to sustainable design. By utilising technologies that reduce water usage, structures can significantly lower their environmental footprint.
- Sustainable Building Materials: The selection of eco-friendly resources is critical. This principle promotes the use of resources that are renewable, recyclable, and possess a reduced environmental effect.
The seven principles of sustainable construction not only provide a framework for attaining sustainability in building projects but also correspond with the increasing demand for eco-friendly solutions in the market. For example, the U.K. market for eco-friendly construction is expected to hit £99.8 billion by 2025, indicating a transition towards more accessible and affordable green options. As misunderstandings regarding the expenses of eco-friendly structures are questioned, the advantages of these methods are progressively acknowledged, clearing the path for a more environmentally-conscious future in development.
Furthermore, it is important to note that carbon in construction accounts for 15% of global greenhouse gas emissions, emphasising the urgent need for eco-friendly practices. As highlighted by Global Newswire, there has been a growing demand for environmentally friendly and eco-conscious solutions in the non-residential green structure market, further emphasising the importance of these principles.
In-Depth Exploration of Each Principle
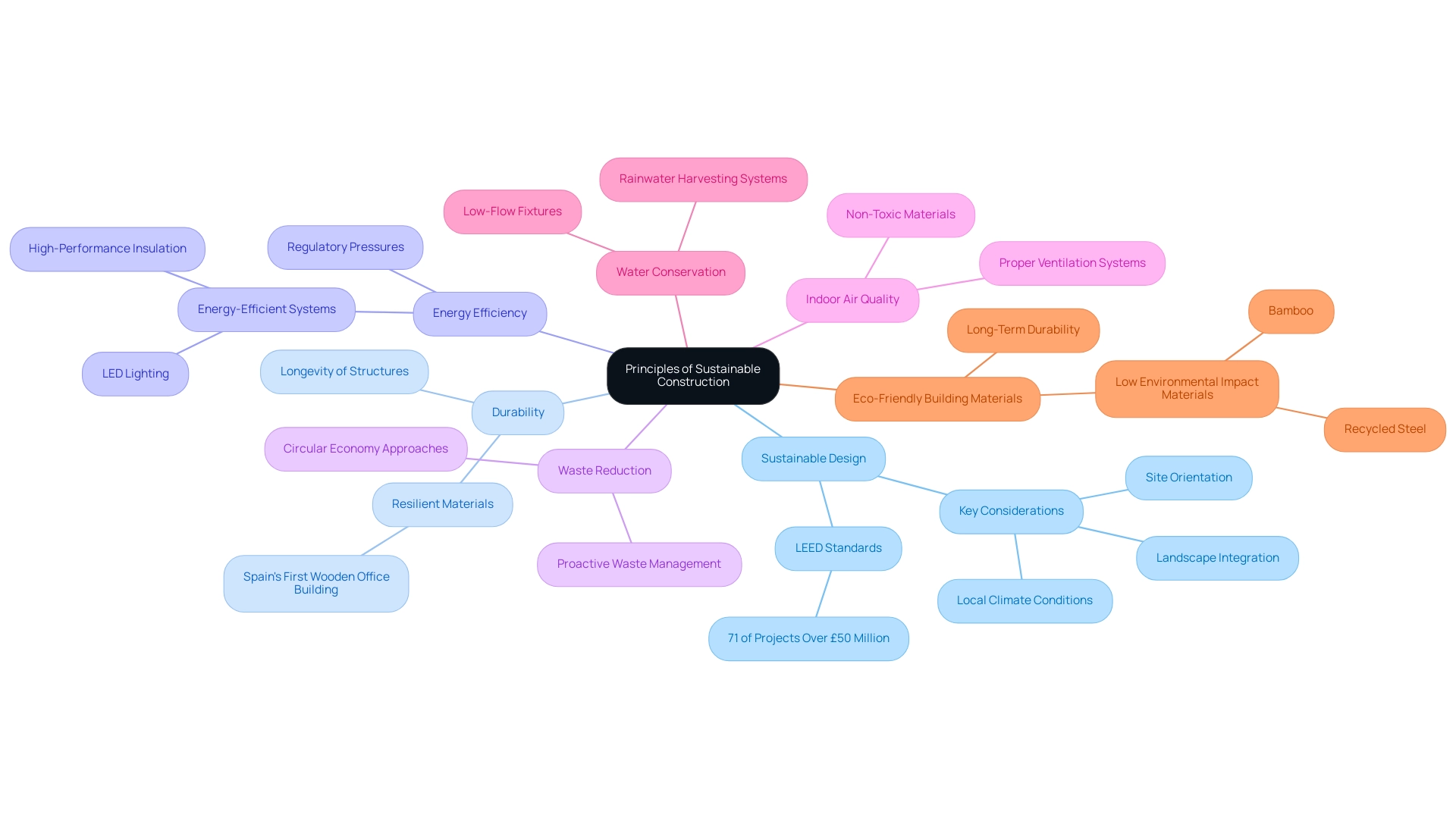
- Sustainable Design: This principle emphasises the critical need to harmonise buildings with their natural environments. Key considerations encompass site orientation, landscape integration, and local climate conditions, collectively enhancing energy efficiency and occupant comfort. By 2025, sustainable design has become increasingly recognised as a vital factor in project specifications, with 71% of projects valued at £50 million and above referencing standards. This statistic underscores the growing importance of adhering to established sustainability benchmarks in large-scale construction projects.
- Durability: The longevity of structures is paramount; durable designs minimise the frequency of repairs and replacements, ultimately reducing lifecycle costs. Industry trends reflect this emphasis on durability, as the integration of resilient materials becomes standard practice. The use of durable building materials not only supports sustainability goals but also ensures that structures withstand environmental stresses over time.
- Energy Efficiency: Implementing energy-efficient systems, such as LED lighting and high-performance insulation, is essential for reducing overall energy consumption. The building sector is experiencing a shift towards energy-efficient designs, driven by regulatory pressures and a growing awareness of environmental impacts. This trend aligns with the broader movement towards sustainability, where energy efficiency serves as a cornerstone of modern construction practices.
- Waste Reduction: A proactive waste management plan during construction can significantly decrease the amount of waste sent to landfills. By embracing circular economy approaches, the industry is advancing towards reducing waste creation and enhancing resource reuse, which is crucial for enduring development.
- Indoor Air Quality: Ensuring optimal indoor air quality is vital for occupant health and well-being. This can be achieved through proper ventilation systems and the use of non-toxic materials, contributing to healthier indoor environments. As awareness of indoor air quality grows, it is becoming a key consideration in eco-friendly design.
- Water Conservation: The installation of low-flow fixtures and rainwater harvesting systems plays a significant role in reducing water usage. With increasing concerns over water scarcity, eco-friendly building methods are prioritising water conservation measures to ensure responsible resource management.
- Eco-Friendly Building Materials: The selection of materials with low environmental impact, such as bamboo or recycled steel, is fundamental to achieving sustainability goals. These materials not only lessen the ecological impact of building projects but also provide long-term advantages in terms of durability and performance. As the sector evolves, the emphasis on sustainable materials is anticipated to strengthen, indicating a commitment to eco-friendly practices.
In summary, the tenets of the seven principles of sustainable construction are not mere trends but essential practices shaping the future of the industry. Recent case studies, including those highlighting sustainability in urban initiatives, reveal that the development sector increasingly acknowledges the significance of these principles for creating resilient, efficient, and eco-friendly structures.
Benefits of Adopting Sustainable Construction Principles
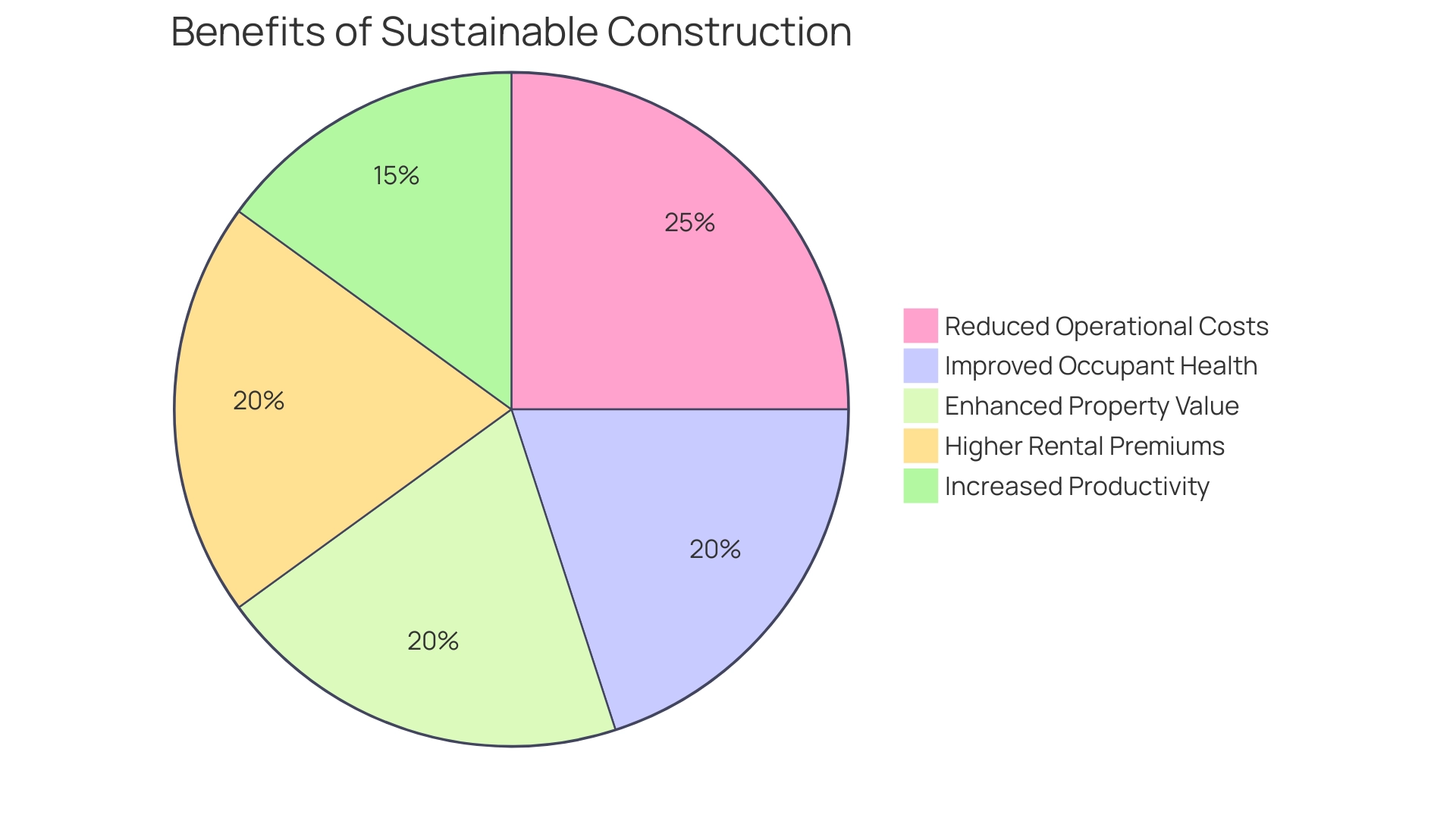
Adopting the seven principles of sustainable construction presents a wealth of advantages, including reduced operational costs, improved occupant health, and enhanced property value. Structures designed with energy efficiency at their core can significantly lower energy bills, resulting in substantial cost savings over time. Furthermore, eco-friendly buildings promote healthier living and working conditions, which can boost occupant productivity and overall well-being.
Research indicates that enhanced indoor air quality and natural lighting in these structures can lead to a 15% increase in productivity among occupants. This is particularly relevant in sectors such as hospitality, where guest satisfaction is paramount. Properties that prioritise sustainability are increasingly appealing to investors and tenants alike, driving higher market values and occupancy rates. In fact, eco-friendly structures have been shown to command rental premiums of up to 20% compared to their traditional counterparts.
This trend is supported by a growing body of evidence that emphasises the economic benefits of eco-friendly practices. Expert opinions reinforce these conclusions, with industry leaders noting that the initial investment in green development often results in long-term savings and improved asset value. A recent study revealed that eco-friendly structures not only reduce operational expenses but also contribute to a 50% decrease in CO2 emissions when utilising options like green concrete and recycled materials.
Case studies from Edmond Shipway further illustrate these advantages. For instance, a recent initiative in the hospitality industry, valued at £18.5 million, demonstrated that adopting eco-friendly construction methods led to a 39% rise in revenue share for green buildings in 2023. Additionally, a project valued at £252 million showcased the effectiveness of eco-friendly methodologies in large-scale developments, while another project valued at £20.5 million highlighted the successful integration of furniture, fixtures, and equipment procurement with environmental considerations in mind.
These examples reflect a broader trend where regions are increasingly investing in eco-friendly methods, adapting to various regulatory environments and market demands. Moreover, there has been a heightened demand for environmentally friendly and green solutions in the non-residential eco-conscious building market, challenging the notion that green buildings are excessively costly.
In conclusion, the incorporation of eco-friendly methods, which adhere to the seven principles of sustainable construction, not only benefits the environment but also offers substantial economic advantages, making it an attractive option for developers and investors in the hospitality industry. Edmond Shipway’s commitment to innovative approaches and continuous improvement, as evidenced by their successful case studies and comprehensive consultancy services, further enhances project outcomes and client relationships, positioning them as a leader in promoting eco-friendly building methods.
Challenges in Implementing Sustainable Construction Practices
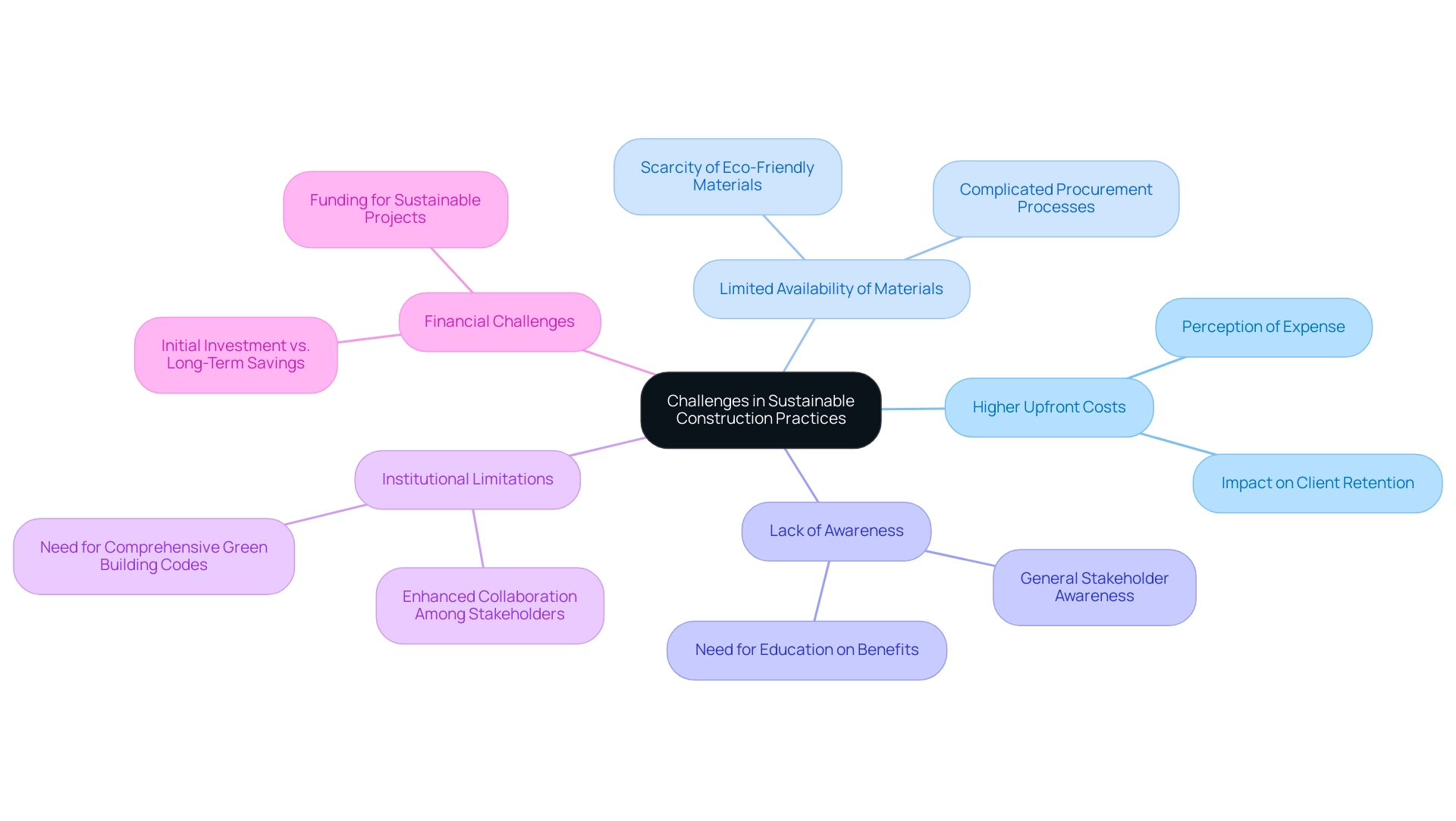
Adopting eco-friendly building methods presents a range of challenges that industry experts must navigate. Among the key obstacles are:
- Higher upfront costs
- Limited availability of eco-friendly materials
- General lack of awareness among stakeholders
Recent data reveals that 87% of building firms recognise client retention as a driving force behind their sustainability initiatives, underscoring the growing importance of these efforts in maintaining a competitive edge.
Many industry professionals perceive eco-friendly methods as more expensive, which can foster resistance to change. This perception is exacerbated by the scarcity of eco-friendly materials, complicating procurement processes and extending project timelines. A study categorising the challenges of eco-friendly development identified institutional limitations as the most significant barrier, highlighting the urgent need for comprehensive green building codes and enhanced collaboration among stakeholders.
The Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin (KMO) measure of sampling adequacy was reported at 0.915, indicating high confidence in the data analysis concerning these challenges. To effectively address these obstacles, it is essential to educate stakeholders about the long-term benefits of sustainability, which can encompass reduced operational costs and increased project value. Fostering teamwork among suppliers, contractors, and clients is vital for developing a shared understanding of eco-friendly methods and their advantages.
Successful examples of eco-friendly building projects demonstrate that, despite high initial expenses, these challenges can be surmounted with the right approach. By confronting these issues head-on, the building sector can make significant strides in adopting more eco-friendly practices, ultimately benefiting both the environment and the economy.
The Future of Sustainable Construction: Trends and Innovations
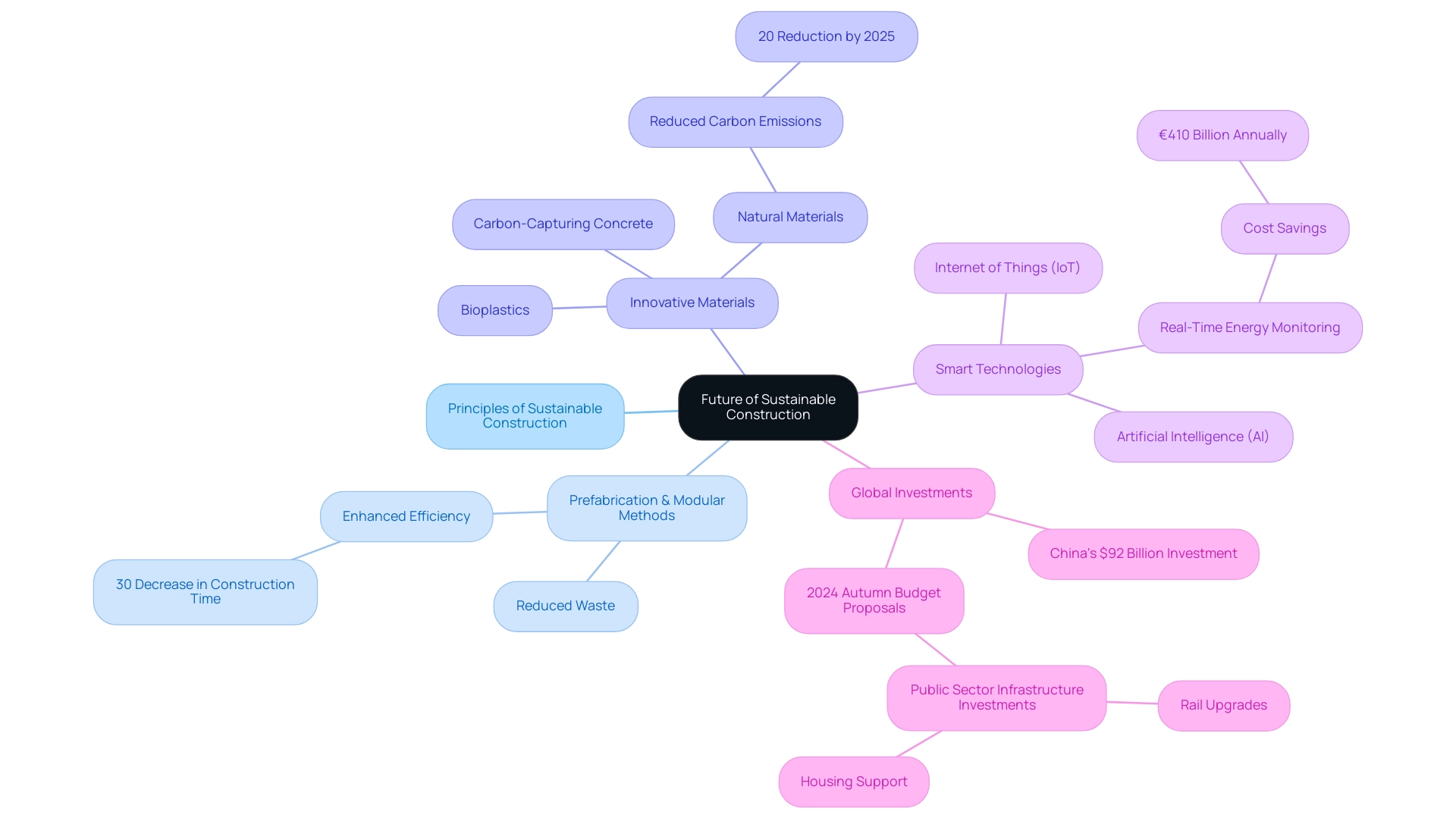
The future of sustainable building stands on the cusp of a significant transformation, propelled by the seven principles of sustainable construction, technological advancements, and a growing commitment to environmental stewardship. A major trend is the rising acceptance of prefabrication and modular methods, which align with these principles by reducing waste and enhancing efficiency throughout the construction process. For example, these methods can decrease construction time by as much as 30%, enabling projects to be completed more swiftly and with a reduced environmental footprint.
Innovations in construction materials are also leading this evolution. Materials such as carbon-capturing concrete and bioplastics are gaining momentum, offering eco-friendly alternatives to traditional options. The building industry is experiencing a shift toward these sustainable materials, which adhere to the seven principles of sustainable construction and can significantly diminish carbon emissions associated with building projects.
Indeed, the use of sustainable materials has the potential to lower global construction-related emissions by 20% by 2025. A case study underscores the extensive use of raw materials in construction, highlighting the environmental impact of conventional materials like concrete and steel, and the potential advantages of adopting natural materials and innovative practices to substantially reduce carbon emissions.
Moreover, the integration of smart technologies, including the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI), aligns with the seven principles of sustainable construction and is poised to revolutionise energy management and operational efficiency in buildings. These technologies facilitate real-time monitoring and optimisation of energy usage, leading to significant cost savings. A recent analysis reveals that employing the latest eco-friendly technologies in construction could save approximately €410 billion annually on global energy expenditures.
As the construction industry adapts, embracing the seven principles of sustainable construction will be essential for meeting sustainability goals and addressing the evolving demands of a more environmentally conscious society. The proposed investments in public sector infrastructure in the 2024 Autumn Budget, including rail upgrades and housing support, further highlight the significance of sustainable practices in future developments.
By prioritising these trends, stakeholders can ensure that their projects not only satisfy current standards but also pave the way for a greener future.
Conclusion
Sustainable construction stands as a pivotal approach to confronting the pressing environmental challenges of our time. By integrating innovative strategies such as resource efficiency, energy conservation, waste management, and the use of sustainable materials, the construction industry can significantly diminish its ecological footprint while amplifying societal benefits. The principles of sustainable construction, spanning durable design to efficient water management, are not mere trends; they are essential practices that will shape the future of the industry.
The advantages of adopting these sustainable practices are numerous. They not only lead to reduced operational costs and enhanced occupant health but also elevate property values and market appeal. As evidence mounts regarding the economic benefits of sustainability, the construction sector increasingly acknowledges the importance of these principles in creating resilient, efficient, and environmentally friendly buildings.
Nonetheless, challenges persist in the widespread implementation of sustainable construction practices. Higher upfront costs, limited material availability, and a lack of awareness among stakeholders can impede progress. Overcoming these obstacles necessitates a concerted effort to educate all parties involved and to foster collaboration within the industry.
Looking forward, the future of sustainable construction is promising, propelled by technological advancements and a growing commitment to environmental stewardship. Innovations such as prefabrication, smart technologies, and eco-friendly materials are poised to revolutionise the industry, paving the way for a more sustainable built environment. As the construction sector adapts to these changes, it possesses the potential not only to meet current demands but also to create a lasting impact for future generations. Embracing sustainable construction is not merely an opportunity; it is an imperative for building a resilient and responsible future.
Share


